Understand
Buddhism, a profound and ancient religion, traces its roots back to the 5th century BC. The founder, Sakyamuni Buddha, was born in Lumbini, near the border of India and Nepal. He renounced his privileged life as a prince in search of true inner peace. After years of contemplation and meditation, he awakened to profound insights that led to the foundation of Buddhism. For centuries, Buddhism thrived in India, supported by great kings and revered as a major religion. However, it faced challenges and suffered the destruction of significant centers, such as the renowned Nalanda University. Despite these setbacks, Buddhism persisted, particularly in the Himalayan regions. Buddhism is divided into two main schools: Theravada and Mahayana. Theravada focuses on personal liberation from suffering, while Mahayana emphasizes the liberation of all beings. A related school, Vajrayana, also known as Tibetan Buddhism, shares the same philosophy but employs different practices. Across all schools, wisdom and compassion are core values, guiding followers in their interactions with the world. Buddhists recognize karma as the governing principle that shapes our existence in the illusory universe of samsara.
Understand
Hinduism, one of the oldest religions in the world, is widely practiced in the subcontinent. Hindus believe in the concept of dharma, or truth, and the cycle of rebirth. According to Hindu philosophy, the actions of individuals in one life will determine their destiny in the next. Hinduism may appear to have many gods, but they are all considered different manifestations of the supreme spirit, Brahma, Vishnu, and Shiva. These gods are worshiped in elaborately decorated temples, where priests perform rituals and prayers. The holy Ganges river holds deep significance for Hindus, who believe that bathing in its waters can cleanse them of their sins. Millions of pilgrims travel to Varanasi and Haridwar to take part in this sacred practice. While the majority of Hindus reside in India, Nepal, and Sri Lanka, there are also Hindu communities in North America, Europe, and the Middle East. Nepal is the only country in the world with Hinduism as its official religion, although there is also a significant Buddhist population.
Understand
Islam, founded by the Prophet Mohammed in 570 AD, means submitting to the will of God. Muslims believe that Mohammed received revelations from the archangel Gabriel, declaring the existence of one God. Initially, Mohammed faced opposition for his teachings, which were seen as a threat to the prevalent kaaba-based religion. In 622 CE, he and his followers fled to Medina, marking the start of the Islamic calendar. Islam is not just a religion but a way of life, supported by five pillars: 1) belief in one God and the Prophet Mohammed, 2) five daily prayers, 3) giving alms to the poor, 4) fasting during Ramadan, and 5) making a pilgrimage to Mecca known as the Hajj. Muslims worship in mosques and are called to prayer by the muezzin. Friday is considered a holy day for Muslims, who gather in mosques for prayers and sermons. India has a significant Muslim population, with many important Islamic sites located in the country. The majority of Indian Muslims follow the Sunni sect, while there is also a sizeable Shia community in certain regions.
Understand
Sikhism originated in the state of Punjab in Northern India during the 16th century. The teachings of Guru Nanak and his successors form the foundation of Sikh philosophy, known as Gurmat. Guru Nanak, born as a Hindu, believed in unity among people of different religions and focused on their actions and beliefs rather than rituals and ceremonies. The Sikh holy book, the Guru Granth Sahib, contains the teachings of the Gurus. Sikhs worship in Gurudwaras, which serve as gateways to the Guru. Unlike other religions, Sikhism has no priests, and members of the congregation can participate in services. Sikhs are a significant majority in Punjab, comprising around 65% of the state's population. While most Sikhs reside in India, there are also large Sikh communities in Canada, the United Kingdom, the Middle East, East Africa, Southeast Asia, and other parts of the world.
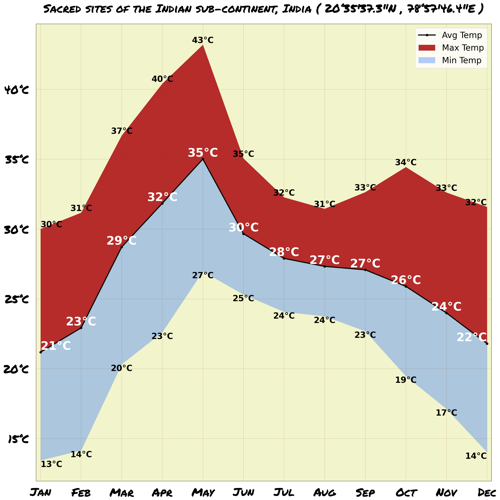
Map & Climate
Popular Foods
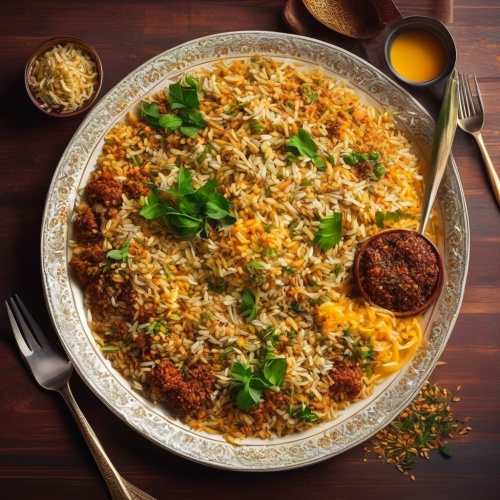 Dish: Butter Chicken (Murgh Makhani)Butter chicken is a rich and creamy curry made with marinated chicken pieces cooked in a tomato-based sauce. The dish originated in the Indian subcontinent and gained popularity in Canada due to the large population of Indian immigrants. It's typically served with basmati rice and naan bread. Butter chicken contains meat – chicken.
Dish: Butter Chicken (Murgh Makhani)Butter chicken is a rich and creamy curry made with marinated chicken pieces cooked in a tomato-based sauce. The dish originated in the Indian subcontinent and gained popularity in Canada due to the large population of Indian immigrants. It's typically served with basmati rice and naan bread. Butter chicken contains meat – chicken.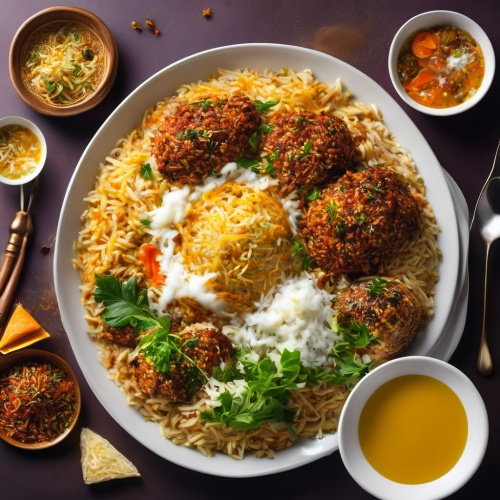  Dish: BiryaniBiryani is a popular rice dish made by cooking Basmati rice with meat (usually chicken, goat, or fish), vegetables, yogurt, and a blend of spices. It originates from the Indian subcontinent and is often considered the national dish of Pakistan. It's known for its flavorful layers and distinct aroma. Biryani contains meat – primarily chicken, goat, or fish.
Dish: BiryaniBiryani is a popular rice dish made by cooking Basmati rice with meat (usually chicken, goat, or fish), vegetables, yogurt, and a blend of spices. It originates from the Indian subcontinent and is often considered the national dish of Pakistan. It's known for its flavorful layers and distinct aroma. Biryani contains meat – primarily chicken, goat, or fish.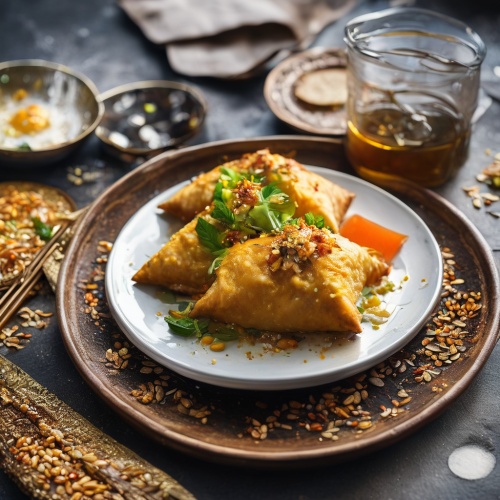  Dish: SamosasSamosas are deep-fried or baked pastry snacks filled with a savory mixture of spiced potatoes, onions, peas, and sometimes meat. They originate from South Asia and have become a popular street food across India. Often served as an appetizer or a quick snack, samosas can be found at roadside stalls, train stations, and even weddings. Samosas can contain meat – typically potatoes, onions, and peas, but some varieties may include meat such as chicken or lamb.
Dish: SamosasSamosas are deep-fried or baked pastry snacks filled with a savory mixture of spiced potatoes, onions, peas, and sometimes meat. They originate from South Asia and have become a popular street food across India. Often served as an appetizer or a quick snack, samosas can be found at roadside stalls, train stations, and even weddings. Samosas can contain meat – typically potatoes, onions, and peas, but some varieties may include meat such as chicken or lamb. 



Comments
NO COMMENTS