Understand
Medina, the second holiest city of Islam, holds immense historical significance. It was here that the Prophet Muhammad migrated from Mecca and taught for several years before his triumphant return. Medina is an integral part of the Hajj and Umrah pilgrimage, attracting millions of devoted Muslims. It served as the birthplace of various Islamic models, such as the Islamic Political Model (Caliphate or Khilafat) and the Islamic Economic Model (interest-free, commodity currency system). These pioneering frameworks provided alternatives to capitalism and socialism, making Medina a hub of innovation and enlightenment. The city of Medinah is not only known for its historical importance, but also for being the resting place of the Prophet Muhammad. The magnificent green dome, a spiritual beacon, attracts countless pilgrims from around the world every year for over 1,400 years. Along with the dome, Medina houses several other sacred sites, including Jannat Al Baqee, Uhud Mountain, Masjid Ghamama, and Masjid Qiblatain, all cherished for their connection to the Prophet Muhammad and his companions. Medina's full name, "Al Madinah Al Monawarah," translates to "the lighting city" or "the city of light." This name was bestowed upon the city after the prophet's migration in 621 A.D. Previously known as "Yathreb," Medina stands as a testament to the profound impact of the Prophet Muhammad and the birthplace of Islamic civilization.
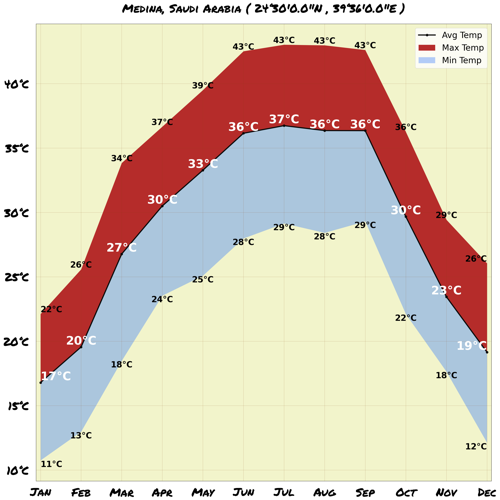
Map & Climate
Popular Foods
 Kabsa is a traditional Saudi Arabian dish made with fragrant basmati rice, meat (usually chicken or lamb), vegetables, and an array of aromatic spices. The dish is cooked in a large pot, often decorated with intricate patterns etched into the surface of the pot, and typically served communally from a shared platter.
Kabsa is a traditional Saudi Arabian dish made with fragrant basmati rice, meat (usually chicken or lamb), vegetables, and an array of aromatic spices. The dish is cooked in a large pot, often decorated with intricate patterns etched into the surface of the pot, and typically served communally from a shared platter.  Shawarma is a Middle Eastern street food favorite in Saudi Arabia, consisting of marinated meat (often chicken, beef, or lamb) that is slowly roasted on a vertical spit. Once cooked, the thin slices of meat are stuffed into pita bread, garnished with fresh vegetables and sauces, and served as a sandwich or wrap. Vegetarian options are also available with grilled vegetables or falafel.
Shawarma is a Middle Eastern street food favorite in Saudi Arabia, consisting of marinated meat (often chicken, beef, or lamb) that is slowly roasted on a vertical spit. Once cooked, the thin slices of meat are stuffed into pita bread, garnished with fresh vegetables and sauces, and served as a sandwich or wrap. Vegetarian options are also available with grilled vegetables or falafel.  Falafel is a popular vegetarian dish made from mashed chickpeas or fava beans, herbs, and spices formed into small balls or patties. They can be eaten as a snack, appetizer, or part of a meal, and are commonly found in sandwiches (like shawarma) or served alongside salads, hummus, and other mezze-style dishes.
Falafel is a popular vegetarian dish made from mashed chickpeas or fava beans, herbs, and spices formed into small balls or patties. They can be eaten as a snack, appetizer, or part of a meal, and are commonly found in sandwiches (like shawarma) or served alongside salads, hummus, and other mezze-style dishes.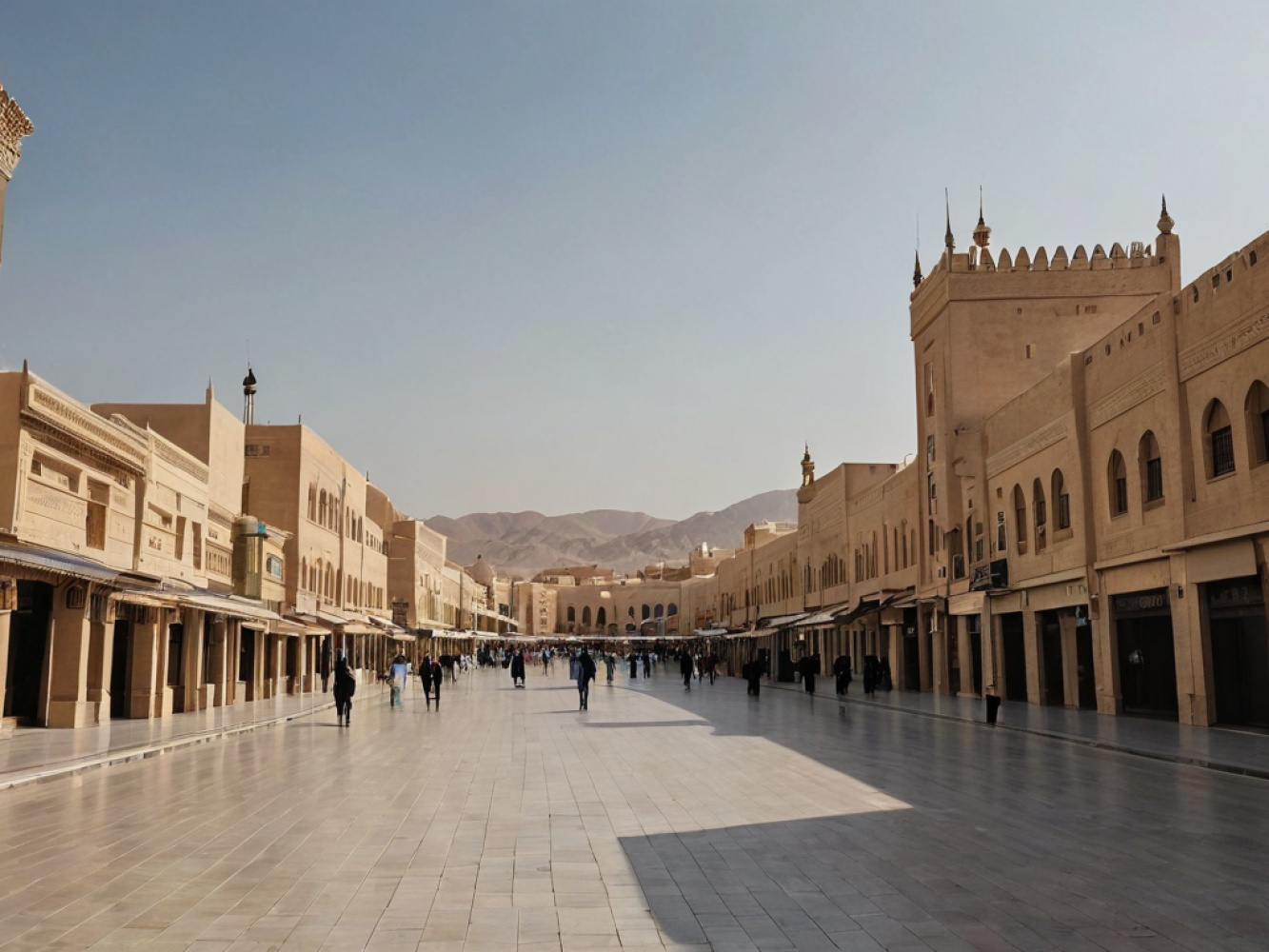 



Comments
NO COMMENTS