Understand
Gilgit-Baltistan, an expansive region covering 72,971 km (28,174 mi), is a breathtakingly mountainous paradise. Nestled within this awe-inspiring landscape is the ancient administrative center of Gilgit, a city of great historical significance. Gilgit was a pivotal stop along the famous Silk Road, a legendary trade route that connected India to the rest of Asia, facilitating the spread of Buddhism. The echoes of the past can still be heard in Gilgit, as numerous Buddhist Sanskrit texts, including the long version of the Heart Sutra, have been discovered here. Gilgit also finds mention in Ptolemy's ancient accounts, with the Dards and Cizinas being among its prominent peoples. The region has been traversed by renowned travelers Faxian and Hsuan Tsang, adding to its mystique. With a rich and complex history, Gilgit witnessed the rise and fall of dynasties, including the Trakane Dynasty and Khushwakhte Dynasty, who led rebellions against various rulers. British rule eventually came to Gilgit in 1889, uniting it with neighboring Hunza and Nagar in the Gilgit Agency. However, the story of Gilgit didn't end there. As British India was granted independence and divided into India and Pakistan, the fate of Gilgit became entangled in a larger conflict. The region became a battleground, claimed by both India and Pakistan, and remains enmeshed in the ongoing Kashmir conflict.
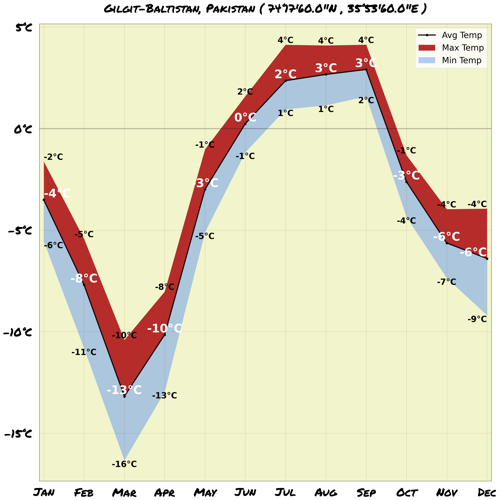
Map & Climate
Popular Foods
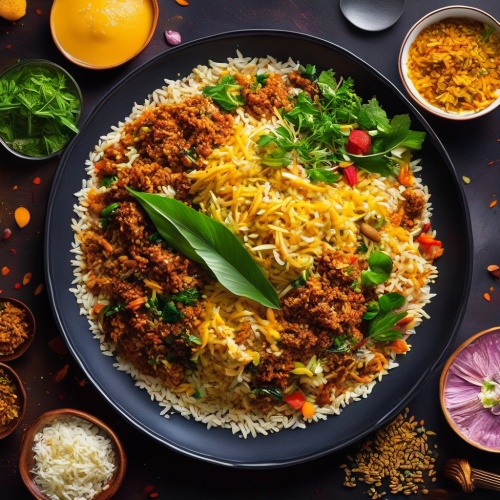 Biryani - A flavorful rice dish made with meat, typically chicken or lamb, cooked with spices and vegetables. The dish is known for its rich aroma and distinct taste, often prepared for special occasions or festive meals.
Biryani - A flavorful rice dish made with meat, typically chicken or lamb, cooked with spices and vegetables. The dish is known for its rich aroma and distinct taste, often prepared for special occasions or festive meals.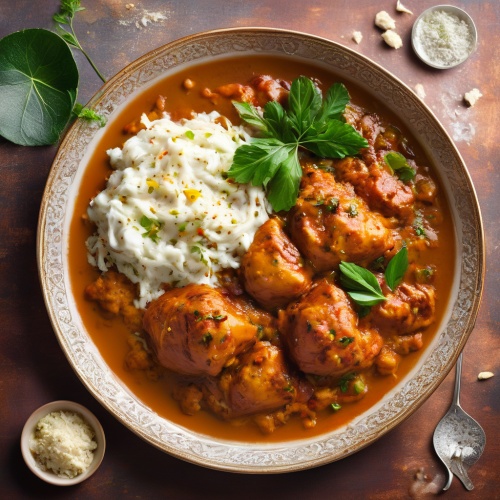 Chicken Tikka Masala - Consisting of roasted marinated chicken chunks simmered in a creamy tomato-based gravy, seasoned with a blend of spices. This dish is mildly spiced and loved for its comforting and delicate flavors.
Chicken Tikka Masala - Consisting of roasted marinated chicken chunks simmered in a creamy tomato-based gravy, seasoned with a blend of spices. This dish is mildly spiced and loved for its comforting and delicate flavors.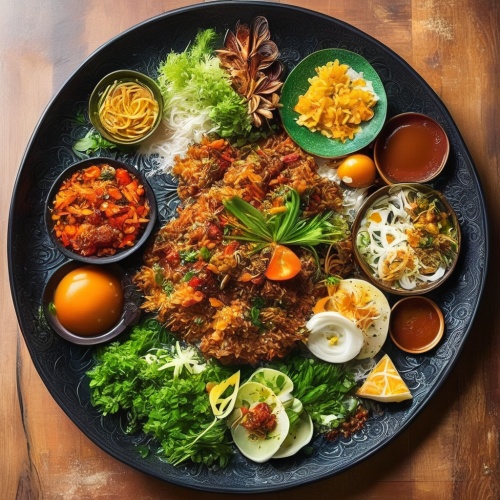 Kabuli Pulau - A delectable rice dish featuring succulent meat, traditionally goat but also available with chicken, cooked with aromatic herbs and spices. The dish is characterized by its colorful presentation, with the rice dyed a distinctive blue hue and garnished with raisins, almonds, and other fruits.
Kabuli Pulau - A delectable rice dish featuring succulent meat, traditionally goat but also available with chicken, cooked with aromatic herbs and spices. The dish is characterized by its colorful presentation, with the rice dyed a distinctive blue hue and garnished with raisins, almonds, and other fruits.



Comments
NO COMMENTS